Doctor Explains Why More Men Are Dying From Covid-19

Subscribe to our new Telegram channel for the latest updates on COVID-19 and other issues.
Men, the elderly, and smokers are most at-risk for Covid-19. We’ve known that since the start. In the beginning of the outbreak, this was the observed pattern. Death rates for men were significantly higher than for women in all countries affected.
It makes sense that a respiratory disease would be more fatal to those who have a weakened respiratory system, like smokers and the elderly. But why men?
Dr Sara Kayat, a UK-based practising NHS and private GP, shared some of her theories as to why the novel coronavirus appears deadlier for men.
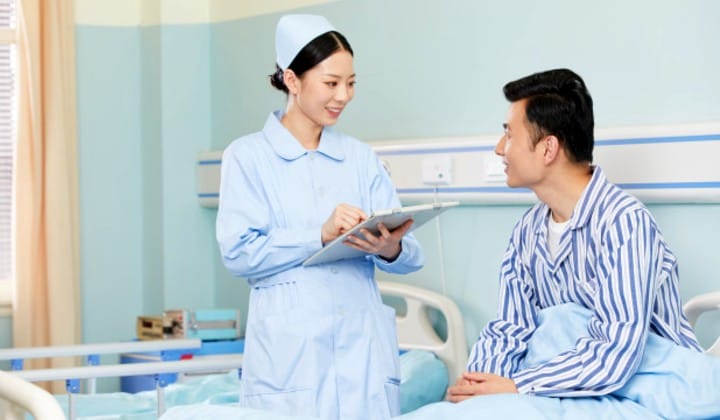
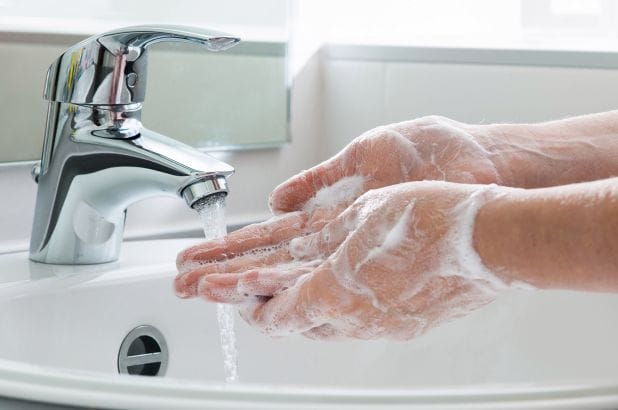
1. Hand-washing habits
The World Health Organisation has continually advised to frequently wash your hands with soap as the best and most cost-effective method to control the spread of Covid-19.
However, studies suggest that men tend to wash their hands with soap less often than women. While a recent study concluded that on average, most countries’ hand-washing habits increased, there was still a noted difference as 57% of women were more likely to adopt increased hand-washing and hand-sanitising behaviour, compared to just 51% of men.

2. Reluctant to seek help
Men tend to not seek help, and this includes medical advice as well. Studies show that they are less likely to acknowledge illness and less likely to visit a healthcare professional when they are sick.
Studies suggest that being ill is regarded as ‘weak’, while risk-taking behaviours are a masculine trait, indicating that men would rather bet on recovering from the illness on their own instead of seeking medical help.
3. Immune system responses
Women’s bodies provoke a greater immune response to viral attacks then men. Women are generally able to quickly clear a virus and reduce its viral load faster than men due to a more efficient immune system.
It’s also the reason why women are more likely to suffer greatly from autoimmune conditions, where “self-reactive” antibodies produced end up attacking the body’s own tissue.
However, in the case of Covid-19, men’s slower immune system would be less effective in clearing out the virus.

4. Hormones
Studies have shown that a person’s immunity to viruses changes with hormone concentrations in the body. For women, this is affected by the menstrual cycle, contraception, pregnancy, or menopause.
It’s proposed that the female hormone oestrogen may contribute to immunity. The theory was tested in mice, where female mice had their ovaries removed and treated with a chemical that blocked the effects of oestrogen. These mice were then found to be more susceptible to SARS than regular female mice, implying the oestrogen hormone’s protective effect.
Since SARS and Covid-19 share 79% of the same genetic sequencing, it’s possible that the same effect could apply to Covid-19.
5. X chromosomes
A study shows that a significant number of gene regulating immune response is coded into our X chromosomes. While the concept is still theoretical, it may explain why the male and female immune system functions differently.
Women have two X chromosomes (XX) while men have only one (XY), so it’s possible that the second X chromosomes that women have confers some sort of immunity advantage.
Of course, these are just possible theories to explain the significant different in death rate between men and women afflicted with Covid-19. However, all these factors possibly play a part.
The important thing to do now is to take care, wash your hands, and abide by the movement control order to prevent further spread of Covid-19.
Keep up to date with the COVID-19 outbreak in Malaysia on our Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Anne is an advocate of sustainable living and the circular economy, and has managed to mum-nag the team into using reusable containers to tapau food. She is also a proud parent of 4 cats and 1 rabbit.